Microsoft HP ROK Windows Server 2008 Standard R2 Edition Inc 5 CAL 1-4 CPU NEW





And Genuine - HP ROK Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2. Builds on the award-winning foundation of Windows Server 2008, expanding existing technology and adding new features to enable IT professionals to increase the reliability and flexibility of their server infrastructures. New virtualization tools, Web resources, management enhancements, and exciting Windows 7 integration help save time, reduce costs, and provide a platform for a dynamic and efficiently managed data center. Powerful tools such as Internet Information Services (IIS) version 7.5, updated Server Manager and Hyper-V platforms and Windows PowerShell version 2.0 combine to give customers greater control, increased efficiency and the ability to react to front-line business needs faster than ever before.
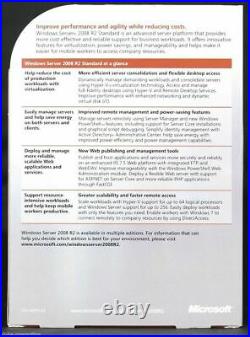
What's New in Windows Server 2008 R2. Windows Server 2008 R2 delivers valuable new functionality and powerful improvements to the core Windows Server operating system to help organizations of all sizes increase control, availability, and flexibility for their changing business needs. New Web tools, virtualization technologies, scalability enhancements, and management utilities help save time, reduce costs, and provide a solid foundation for your information technology (IT) infrastructure. Windows Server 2008 R2 includes many enhancements that make this release the most robust Windows Server Web application platform yet. It offers an updated Web server role, Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.5, and greater support for. Virtualization is a major part of today's data centers. The operating efficiencies offered by virtualization allow organizations to dramatically reduce operational effort and power consumption. Windows Server 2008 R2 provides the following virtualization types: Client and Server virtualization provided by Hyper-V and Presentation virtualization with Remote Desktop Services. Windows Server 2008 R2 is capable of unprecedented workload size, dynamic scalability, and across-the-board availability and reliability. A host of new and updated features will be available, including leveraging sophisticated CPU architectures, increased operating system componentization, and improved performance and scalability for applications and services. The ongoing management of servers in the data center is one of the most time-consuming tasks facing IT professionals today.Any management strategy you deploy must support the management of both your physical and virtual environments. To help with this problem, Windows Server 2008 R2 has new features to reduce the ongoing management of Windows Server 2008 R2 and to reduce the administrative effort for common day-to-day operational tasks.
Better Together with Windows 7. Windows Server 2008 R2 has many features that are designed specifically to work with client computers running Windows 7. Windows 7 is the next version of the Windows client operating system from Microsoft. Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard.
Is the most robust Windows Server operating system to date. With built-in, enhanced Web capabilities and included virtualization technology, Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard is designed to increase the reliability and flexibility of your server infrastructure while helping save time and reduce costs. Enhanced security features help protect your data and network, and provide you with a solid, highly dependable foundation for your business.
Additionally, powerful tools give you greater control over your servers and streamline configuration and management tasks. Web, Virtualization, Security, Reliability, and Productivity. Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard provides organizations with the ability to deliver rich Web-based experiences efficiently and effectively, with improved administration and diagnostics, advanced development and application tools, and lower infrastructure costs. Internet Information Services 7.5. Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard is a powerful Web application and services platform.
The Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.5 in Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard delivers a completely modular, extensible Web server with expanded application hosting, while retaining excellent compatibility and solving key customer challenges. Many organizations find that patch management, resource utilization, maintenance costs, and server sprawl are among their biggest challenges. Server virtualization technologies, including Windows Server Hyper-V and enhancements to Remote Desktop Services, can help meet all of these challenges by helping you consolidate your resources and realize significant infrastructure and management cost savings.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V is the hypervisor-based virtualization feature included as a role of Windows Server 2008 R2. It contains everything needed to support machine virtualization. Hyper-V enables IT organizations to reduce costs, to improve server utilization, and to create a more dynamic IT infrastructure. Hyper-V provides the greater flexibility because of dynamic, reliable, and scalable platform capabilities combined with a single set of integrated management tools to manage both physical and virtual resources, which enables you to create an agile and dynamic datacenter and progress toward achieving self-managing dynamic systems. Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard provides a security-enhanced, easy-to-manage platform for delivering access to centrally managed applications and resources from the Internet by using HTTPS; you do not need to provide access through a virtual private network (VPN) or by opening unwanted ports on firewalls.Application virtualization separates the application configuration layer from the operating system. It enables applications to run on clients--including desktops, servers, and laptops--without being installed, and allows applications to be administered from a central location. This enables you to run applications that otherwise may not be able to coexist on the same server. Improved Data Center Power Consumption and Streamlining Management. Improved data center power consumption management.
With the proliferation of physical computers in data centers, power consumption is of paramount importance. In addition to the cost-saving associated with reducing power consumption, many data centers are constrained by the number of computers they can support in their data center by the actual power available to the data center. Therefore reducing your power consumption also allows you to support more physical computers while using the same amount of power, or less power, than before. Improved Management of File Services. Storage is no longer a marginal expense.Nor is managing storage any longer simply about volume and availability; organizations need to manage their data more effectively as well as more efficiently. Only by gaining insight into their data can companies reduce the cost of storing, maintaining, and managing data. Only by enforcing company policies and knowing how storage is utilized can administrators efficiently use their storage and mitigate the risks of leaking data. The next frontier for administrators is to be able to manage data based on business value. The Windows File Classification Infrastructure (FCI) in Windows Server 2008 R2 provides insight into your data to help you manage your data more effectively, reduce costs, and mitigate risks.
Remote administration of server computers is essential to any efficient data center. It is very rare that server computers are administered locally. Windows Server 2008 R2 introduces a number of improvements in remote administration, including improved remote management through graphical management consoles and improved remote management from command-line and automated scripts. Reduced administrative effort for administrative tasks performed interactively. Reducing administrative effort for day-to-day administrative tasks is another key design goal for Windows Server 2008 R2.
Many of the management consoles used to manage Windows Server 2008 R2 have been updated or completely redesigned to help reduce your administrative effort. Some of the prominent updated and redesigned management consoles are listed in the following table with descriptions of the improvements. Enhanced command-line and automated management by using PowerShell version 2.0. Windows Server 2008 R2 includes PowerShell 2.0, which offers a number of improvements over version 1.0, including the following. Improved remote management by using PowerShell remoting. Improved security for management data, including state and configuration information, by using constrained runspaces. Enhanced GUIs for creating and debugging PowerShell scripts and viewing PowerShell script output by using Graphical PowerShell and the Out-GridView cmdlet.Extended scripting functionality that supports creation of more powerful scripts with less development effort. Improved portability of PowerShell scripts and cmdlets between multiple computers.
Identity management has always been one of the critical management tasks for Windows-based networks. The implications of a poorly managed identity managed system are one of the largest security concerns for any organization. Windows Server 2008 R2 includes identity management improvements in the Active Directory Domain Services and Active Directory Federated Services server roles. Improved compliance with established standards and best practices. Windows Server 2008 R2 includes an integrated Best Practices Analyzer for each of the server roles.
The Best Practices Analyzer creates a checklist within Server Manager for the role, which you can use to help perform all the configuration tasks. A host of new and updated features contribute to this including.
Windows Server 2008 R2 is the first Windows operating system to be offered for only 64-bit processors. Microsoft introduced the concept of server roles to allow server administrators to quickly and easily configure any Windows-based server to run a specific set of tasks and remove extraneous OS code from system overhead. Roles have been refined and feature sets redefined as customers have expressed desires for certain capabilities in popular scenarios. Improved performance and scalability for applications and services. Another key design goal was to provide higher performance for Windows Server 2008 R2 running on the same system resources as previous versions of Windows Server.
In addition, Windows Server 2008 R2 supports increased scaling capabilities that allow you to support greater workloads than ever before. Windows Server 2008 R2 features that improve performance and scalability for applications and services. The ability to quickly access information is more critical today than ever before. The foundation for this high-speed access is based on file services and network attached storage (NAS).Microsoft storage solutions are at the core of providing high-performance and highly available file services and NAS. The release version of Windows Server 2008 introduced many improvements in storage technologies. Windows Server 2008 R2 includes additional improvements that enhance the performance, availability, and manageability of storage solutions. Improved Protection of Intranet Resources.
The Network Policy Server (NPS) is a Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server and proxy and Network Access Protection (NAP) health policy server. NPS evaluates system health for NAP clients, provides RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA), and provides RADIUS proxy functionality. Making the Experience Better Together with Windows 7. Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard has many features that are designed specifically to work with client computers running Windows 7 that include. Simplified remote connectivity for corporate computers by using the DirectAccess feature. One common problem facing most organizations is remote connectivity for their mobile users. One of the most widely used solutions for connecting remote users is a virtual private network (VPN) connection.Depending on the type of VPN, users may need to install VPN client software on their mobile computer and then establish the VPN connection over the Internet. The DirectAccess feature in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 allows Windows 7 client computers to directly connect to intranet-based resources without the complexity of establishing a VPN connection. The user has the same connectivity experience both in and outside of the office. Improved performance for branch offices.
The BranchCache feature in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 Client reduces the network utilization on WAN links that connect branch offices and improve end user experience at branch locations, by locally caching frequently used content on the branch office network. As remote branch clients attempt to retrieve data from servers located in the corporate data center, they store a copy of the retrieved content on the local branch office network.Subsequent requests for the same content are served from this local cache in the branch office, thereby improving access times locally and reducing WAN bandwidth utilization between the branch and corpnet. Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard supports the BranchCache Content Server. This deployment scenario centers around peer content requests and is intended solely for small remote offices, with roughly 5-10 users that don't warrant a dedicated local server resource. In this scenario, the BranchCache server at corpnet receives a client content request, and if the content has been previously requested at the remote site will return a set of hash directions to the content's location on the remote network, usually another worker's computer. Content is then served from this location.
1.4 GHz (x64 processor). DVD-ROM drive; mouse & keyboard. To use Windows Server 2008 R2, you need. Minimum: 1.4 GHz (x64 processor). Note: An Intel Itanium 2 processor is required for Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems.
Maximum: 8 GB (Foundation) or 32 GB (Standard) or 2 TB (Enterprise, Datacenter, and Itanium-Based Systems). Minimum: 32 GB or greater. Foundation: 10 GB or greater. Note: Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM will require more disk space for paging, hibernation, and dump files. 600 or higher resolution monitor. Actual requirements will vary based on your system configuration, and the applications and features you choose to install. Processor performance is dependent upon not only the clock frequency of the processor, but the number of cores and the size of the processor cache. Disk space requirements for the system partition are approximate.Additional available hard disk space may be required if you are installing over a network. You do not need to enter a product key to evaluate any version of Windows Server 2008 R2 software, however activation is required within 10 days.
Failing to activate the evaluation will cause the licensing service to shut down the machine every hour. This is an open box version of Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Edition inc 5 CALs for installation on any system.
This item is in the category "Computers/Tablets & Networking\Software\Operating Systems". The seller is "quality_products17" and is located in this country: GB. This item can be shipped to United Kingdom.
- Model: Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise
- Licence Category: Standard
- Number of Devices: 4
- Unit Quantity: 1
- Format: DVD
- Type: Operating System
- MPN: 589276-B21, 589276-B22
- For Operating Systems: Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2
- Language: English
- Brand: HP